Recent projects::
- Distribution of surface glycoproteins on influenza A virus ::
- Structural organization of a filamentous influenza A virus ::
- Cryo-EM of vitrified endothelial cells ::
Distribution of surface glycoproteins on influenza A virus ::
Abstract (Wasilewski et al., Vaccine 2012)
We use electron cryotomography to reconstruct virions of two influenza A H3N2 virus strains. The maps reveal the structure of the viral envelope containing hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) glycoproteins and the virus interior containing a matrix layer and an assembly of ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs) that package the genome. We build a structural model for the viral surface by locating copies of the X-ray structure of the HA ectodomain into density peaks on the virus surface. We calculate inter-glycoprotein distances and the fractional volume occupied by glycoproteins. The models suggest that for typical HA densities on virus, Fabs can bind to epitopes on the HA stem domain. The models also show how membrane curvature may influence the number of glycoproteins that can simultaneously interact with a target surface of receptors. Read more…
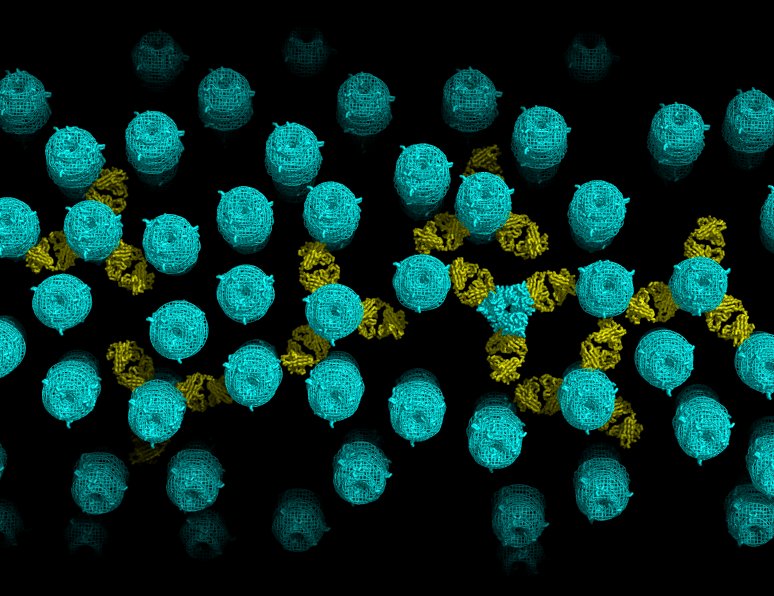
Structural organization of a filamentous influenza A virus ::
Abstract (Calder et al., PNAS 2010)
Influenza is a lipid-enveloped, pleomorphic virus. We combine electron cryotomography and analysis of images of frozen-hydrated virions to determine the structural organization of filamentous influenza A virus. Influenza A/Udorn/72 virions are capsule-shaped or filamentous particles of highly uniform diameter. We show that the matrix layer adjacent to the membrane is an ordered helix of the M1 protein and its close interaction with the surrounding envelope determines virion morphology. The ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs) that package the genome segments form a tapered assembly at one end of the virus interior. The neuraminidase, which is present in smaller numbers than the hemagglutinin, clusters in patches and are typically present at the end of the virion opposite to RNP attachment. Incubation of virus at low pH causes a loss of filamentous morphology, during which we observe a structural transition of the matrix layer from its helical, membrane-associated form to a multilayered coil structure inside the virus particle. The polar organization of the virus provides a model for assembly of the virion during budding at the host membrane. Images and tomograms of A/Aichi/68 X-31 virions show the generality of these conclusions to non-filamentous virions. Read more…
Cryo-EM of vitrified endothelial cells ::
Abstract (Berriman et al., PNAS 2009)
In endothelial cells, the multifunctional blood glycoprotein von Willebrand Factor (VWF) is stored for rapid exocytic release in specialized secretory granules called Weibel-Palade bodies (WPBs). Electron cryomicroscopy at the thin periphery of whole, vitrified human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) is used to directly image WPBs and their interaction with a 3D network of closely apposed membranous organelles, membrane tubules, and filaments. Fourier analysis of images and tomographic reconstruction show that VWF is packaged as a helix in WPBs. The helical signature of VWF tubules is used to identify VWF-containing organelles and characterize their paracrystalline order in low dose images. We build a 3D model of a WPB in which individual VWF helices can bend, but in which the paracrystalline packing of VWF tubules, closely wrapped by the WPB membrane, is associated with the rod-like morphology of the granules. Read more.